RF CABLE
The RF cable is a cable that transmits electromagnetic energy in the RF range. The RF cable is an indispensable component in various radio communication systems and electronic devices. It is widely used in wireless communication and broadcasting, television, radar, navigation, computer and instrumentation.
Overview
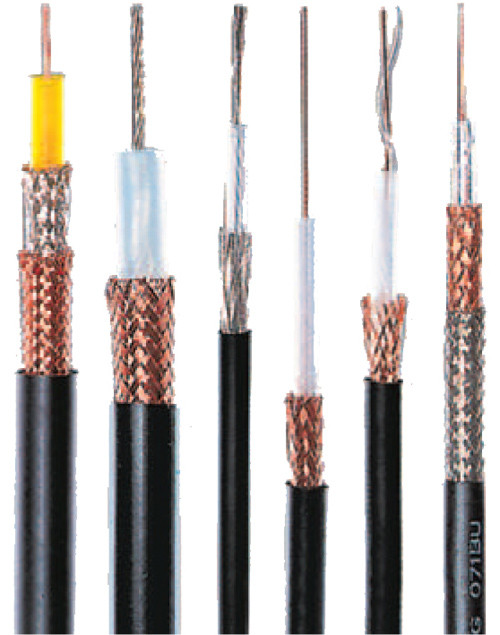
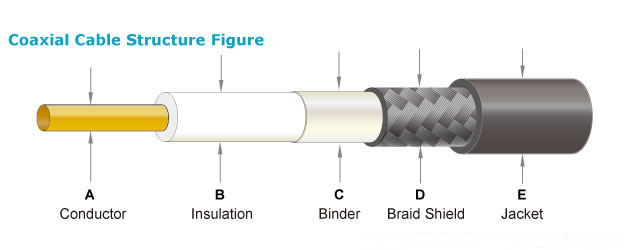
The RF cable, also called the coaxial cable, is composed of a coaxial inner conductor, an outer conductor, and a medium supporting the inner and outer conductors. In radio frequency transmission of radio communication and broadcast television, RF cable is an important measure. If improperly selected, it will not only cause waste, increase investment costs, but also make the system unstable during operation, causing malfunctions and causing equipment damage. In order to properly select the RF cable, you need to learn some parameters and types of the cable. The characteristics of RF cables include electrical and mechanical properties. Electrical properties include characteristic impedance, transmission loss and frequency characteristics, temperature characteristics, shielding characteristics, rated power, and maximum withstand mechanical properties including minimum bending radius and unit length. Allow maximum tensile force and cable aging characteristics and consistency.
Characteristics
1. Can transmit a wide frequency band
2. High degree of defense against external interference
3. Small antenna effect and low radiation loss
4. Simple structure, convenient installation and economical
Classification--The structure of RF cables is varied and can be categorized according to different methods and types.
Classified by structure
(1) Coaxial RF cable
Coaxial RF cables are the most common type of construction. Since the inner and outer conductors are in a concentric position, the electromagnetic energy is confined to propagate in the medium between the inner and outer conductors, so that it has the advantages of small attenuation, high shielding performance, use frequency bandwidth and stable performance. Usually used to transmit RF energy from 500 kHz to 18 GHz.
Currently, there are two types of commonly used RF coaxial cables: 50Ω and 75Ω RF coaxial cables. The characteristic impedance 75Ω RF coaxial cable is commonly used in CATV networks, so it is called CATV cable, and the transmission bandwidth can reach 1GHz. Currently, the transmission bandwidth of common CATV cable is 750MHz.
(2) Symmetrical RF cable
Symmetrical RF cable circuits have an open electromagnetic field. Due to the radiant electromagnetic energy at high frequencies, the attenuation is increased and the shielding performance is poor. In addition, the influence of atmospheric conditions is often used. Symmetrical RF cables are primarily used in the case of low RF or symmetric feeds.
(3) Spiral RF cable
The conductor in the coaxial or symmetrical cable can sometimes be made into a spiral coil shape, thereby increasing the inductance of the cable, thereby increasing the wave impedance of the cable and delaying the transmission time of the electromagnetic energy. The former is called a high resistance cable, and the latter is called a high resistance cable. For delay cables. If the spiral coils are wound at different densities in the length direction, a varistor cable can be made
Classified by insulation type
(1) Solid insulated cable
The solid high frequency dielectric is filled between the inner and outer conductors of such a cable, and most of the soft coaxial RF cables use this type of insulation.
(2) Air insulated cable
In the insulation layer of the cable, most of the volume is air except for a part of the solid medium supporting the inner and outer conductors. Its structural feature is that it does not pass through the dielectric layer from one conductor to the other. Air insulated cables have very low attenuation and are a common type of structure used at ultra high frequencies.
(3) Semi-air insulated cable
This type of construction is an insulation type between the two, the insulation is also a combination of air and solid medium, but from one conductor to the other through the solid medium layer.
Classified by insulation
Plastic insulated cable, rubber insulated cable and inorganic mineral insulated cable.
Classified by softness
Soft cable, flat cable and rigid cable.
Classified by transmission power
Low power below 0.5 kW, medium power of 0.5-5 kW, high power cable of 5 kW or more.
Classified by product use characteristics
Low attenuation, low noise, small size, and stable phase cable
RF cable attenuation
The attenuation of the RF cable is related to the conductor, medium, structural dimensions, process level and frequency of operation.
1. The attenuation constant is larger or worse than 50MHz, and the high frequency has a margin, which is often caused by the aluminum base in the aluminum-plastic composite tape being too thin. When the frequency is relatively low, the thickness of the aluminum base is less than or equal to The transmission depth of the frequency is equivalent, causing the αR to be too large. According to theoretical calculations, the transmission depth of the aluminum layer at f = 50 MHz is 12.2 μm. Generally, taking an aluminum base of 12 to 15 μm can solve this problem. (Of course, if the requirements for shielding attenuation are taken into consideration, it can be appropriately thickened)
2. Selecting the tan δ of PE in the use frequency is large. If it reaches the x×10-3 level, the tan δ of the insulation structure will increase, and the attenuation of the cable will increase. Therefore, we must pay attention to two problems. First, tan δ should be small (for example, tan δ at 400 MHz is 2~4×10-4, the smaller the better), first, the process performance (such as melt index is 0.5~10) should be adapted. Insulating extrusion, different melt indices have different temperatures.
3, the outer conductor weaving is generally 60%-80% is appropriate, the larger the effect on reducing the attenuation is not very obvious.
4. The design and processing of the mold for insulation production is also the key. It should ensure that the product achieves an ideal uniform structure and the equivalent dielectric constant meets the design requirements.
5, physical foaming PE its attenuation is qualified at low frequencies, while high frequency (such as more than 800MHz) is out of tolerance, mostly related to dielectric loss tangent and equivalent dielectric constant, or with outer conductor weaving density Small, the outer diameter of the inner conductor is small. In addition, the attenuation constant also depends on the degree of foaming. Appropriately increase the degree of foaming within the range allowed by the impedance and echo (which can increase the degree of foaming, increase the impedance, and reduce the attenuation). It can help to increase the attenuation constant of the cable, and at the same time reduce the cost.
Selection requirements
When actually selecting an RF cable, its characteristic impedance, rated power, attenuation, and maximum operating voltage can be considered. In the radio frequency transmission of radio communication and broadcast television, the RF impedance, the output power, and the peak voltage that may be reached are combined with the output of the transmitter, and a certain margin is left, and the appropriate cable is selected according to the environmental conditions used. It should be noted that when using the RF cable, it is necessary to match the cable plug, cable socket, and coaxial switch with the same characteristic impedance, and can not be mixed, so as to avoid large wave reflection and form a standing wave in the cable.
When the RF cable is used for medium wave, because of its low operating frequency and low loss, the RF cable originally used on TV can be used in a 50 kW system in a medium wave transmission system, but the current passing through the cable will It is much larger than the TV system of the meter band, so ensure that the cable head and the cable socket are in good contact, otherwise the fault will be caused by overheating.
Send your message to us:
Post time: Aug-13-2018